There is no unequivocal answer to the question "how to choose a greenhouse?". The film, seclo, polycarbonate - all these materials are good in their own way, they have merits and demerits. Therefore, the choice of a greenhouse assumes only an individual approach. It's not always necessary to chase the latest fashion innovations - it often happens that old, time-tested materials will do just fine.
If you decide to acquire your own greenhouse, first you need to determine what exactly you need it for, what kind of crops it is supposed to grow and how much, the period of operation of the greenhouse (season or year round). On this depends the availability of heating in the greenhouse. How much money can you allocate to a greenhouse? How much time and energy are you willing to devote to work? Answers to all these questions will help to choose the right greenhouse, suitable for your needs.
Content
Greenhouse with polyethylene coating
Although such material as polycarbonate is now, as they say, in a trend, good old polyethylene is too early to write off. The film has a lot of advantages - simplicity in work, minimum of labor. If you need to dismantle part of the wall or roof, for example, for ventilation - you can do it very quickly.
For the winter, the film is usually taken off. Of course, this is inconvenient, since every year the film has to be removed and pulled. However, in winter it is not necessary to worry that the greenhouse will bend and collapse under the weight of the snow cover, such as polycarbonate or glass. Thus, if there is no possibility to visit the greenhouse regularly and clean it from snow, the option with a film will be most suitable.
Another advantage of the film coating is, strangely enough, in its absence in the winter. The earth in the greenhouse is covered with a layer of snow, which provides a natural temperature and humidity for the soil microflora. In covered greenhouses without heating, the land in winter is deep freezing, useful microorganisms are dying, so in a covered greenhouse for the winter load a layer of manure, or throw snow from the street. Otherwise, by the beginning of the season, the land simply will not have time to thaw and warm up.
Polyethylene film is an inexpensive material, but it will have to be bought periodically, since almost all types of film for greenhouses completely wear out in a few seasons - polyethylene is destroyed by ultraviolet radiation. The film easily tears, it can even break a strong wind. Although, in comparison with glass, polyethylene film is safer.
Types of films for greenhouses
So what can the garden marketers offer to the modern market?
reinforced polyethylene
It differs from the usual by the presence of a synthetic mesh embedded in the fabric. Such material is quite strong, and it can be safely stretched on a large greenhouse, and not be afraid of hail and strong wind. However, it was not without drawbacks: manufacturers put first of all not strength, but resistance to solar radiation. And it often happens that the film literally crumbles in two or three seasons. Probably, for this reason, the data on the service life are very different - from 2 to 8 years.
polyethylene with additives
The assortment of such films is very extensive, however not every film is suitable for greenhouses. What pleased producers, so it's additives, stabilizers, which protect the surface from the deadly effect of ultraviolet radiation. Of course, such films are 10 times more expensive than usual, but they last longer - up to three years or more. Such a film is usually painted pink or light orange, but not necessarily.
Another very useful additive - luminophore.
It is able to convert ultraviolet radiation to infrared, which has a beneficial effect on plants - growth and photosynthesis processes are more intense, which has a very positive effect on yields. This film is also called light-converting. However, when buying such material, remember that it must also be stabilized, otherwise it will not last very long. For the presence of luminophoric additives, the film can be checked if it is enlightened by an ultraviolet lamp. Through the film, the light from the lamp should be red.
bubble polyethylene
Perhaps, this material is familiar to all. Used mainly for packaging fragile products and electronics. Children are very fond of "bursting" the air bubbles with which the film is covered. However, this material is very popular among the owners of greenhouses - the bubble film passes light well and has excellent thermal insulation properties. And although this film is not longevity, it is perfect for a small guy or a recessed warm garden bed for growing early greens and salad cabbage, flowers, etc.
It should be noted that, very often, manufacturers cheat, tinting the film and giving it out for stabilized. Therefore, before buying it is necessary to demand from the seller a certificate for the goods and inquire about the reputation and reviews of the manufacturer.
films of other materials
A PVC film is perhaps the most suitable option for a greenhouse. In most such films to the touch resemble rubber, have a slightly pinkish or yellowish tinge. PVC film is very strong and durable. Such material can last without removal from the frame of the greenhouse for 6 years or more. PVC film perfectly resists the action of ultraviolet, its only drawback is a high price.
Greenhouses with glass coating
Glass has many advantages:
• High transparency. Remains unlimited time with proper care and washing of the surface.
• Chemical inertness. A very important point, since some films and polycarbonates can release toxic substances into the air during heating, which adversely affects plants.
• Glass is very resistant to abrasive particles. This allows the glass surface to remain virtually flawless for an unlimited time. It is also important that glass can not damage the pesticides used to treat plants. All harmful substances are easily washed off the glass surface with water.
If we talk about shortcomings, first of all we should note the solid weight of the glass. However, weight can be attributed to the benefits, as it gives the greenhouse additional stability, which allows you to save on the frame, making it from a light and inexpensive material. But the design with a film coating can overturn a strong wind if the frame is light.
Glass has a very high thermal conductivity. This means that the greenhouse warms up very quickly and cools down just as quickly. It will always be colder than film. From the observations of experienced truck farmers it follows that in a film-coated greenhouse the crop always ripens about one week earlier than in a glass-covered one.
Another shortcoming of glass is fragility. Large hailstones can in a matter of minutes leave from the glass greenhouse one skeleton. Polyethylene film hail also hurt, but polycarbonate will stand.
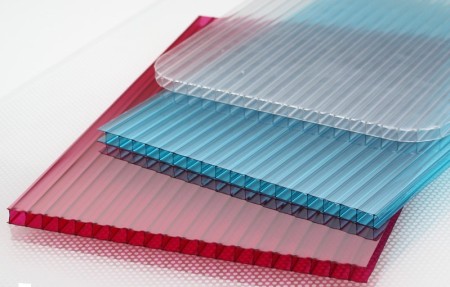
Greenhouses with polycarbonate coating
Polycarbonate is a polymer plastic. It is very durable, but not fragile. The characteristics of this material are similar to those of glass. It is an impact-resistant material with good thermal insulation properties. This is its main advantage over polyethylene and glass. Particularly suitable polycarbonate for year-round greenhouses with heating.
For greenhouses, mainly polycarbonate with honeycombs is used. Its structure consists of several layers, which are joined together by stiffening ribs. Between the layers is air, which provides good thermal insulation.
The polycarbonate sheet has an outer and an inner side. The inside is simple, and the outside is UV protected. When installing polycarbonate sheets, you should monitor the side of the sheet, because if the inner side is on the outside, the polycarbonate is destroyed very quickly.
Polycarbonate is of different quality, which greatly affects its cost. For economy, manufacturers use recycled materials for polycarbonate production. And the cheaper polycarbonate, the more it contains secondary raw materials. Such material in hot weather exudes not the most pleasant smell. They also save on the density of the material, making it less expensive than expensive analogues. Such materials do not last long.
If in winter, under the weight of the snow cover, the greenhouse is bent, the surface should be immediately cleaned of snow, otherwise polycarbonate may crack. If there is no possibility to regularly clean the greenhouse of snow in winter, you need to buy thick sheets, otherwise by spring polycarbonate will crack.
Quality thick polycarbonate is quite expensive. Most models can not be assembled on their own, which means that you will have to pay extra for the assembly of the structure. For a greenhouse with a polycarbonate coating, a foundation is needed. What kind of foundation you can use - we'll explain below.
The best greenhouses of polycarbonate are all-weather, heating. In addition, for light summer greenhouses to use polycarbonate is unreasonably expensive. In hot weather, the temperature inside the polycarbonate greenhouse can exceed 55 degrees, and plants can die from high temperatures. Therefore, it is best to give preference to greenhouses that have doors on both sides. In addition, you can install a forced ventilation system.
Serving polycarbonate is not difficult, the surface should only be washed occasionally with a soft sponge soaked in a solution of soap or detergent. Do not use chlorine and various kinds of solvents and aldehydes.
Another problem faced by owners of polycarbonate greenhouses is the ingress of water into the honeycomb. Water greatly reduces the transparency of the material, polycarbonate begins to turn green. Therefore, it is necessary to choose high-quality, long-life sealants for insulation.
Types of foundations of greenhouses
Do we need a foundation for a greenhouse? This question is rather controversial. On the one hand, the construction on the foundation is more stable. On the other hand, if there is a need to transfer the foundation, difficulties will arise with the dismantling of the foundation. There are also gardeners who are afraid (and, as a rule, not without reason) that a greenhouse without a foundation can simply be stolen.
Below we will consider several types of foundations that can be used for different types of greenhouses.
wooden foundation of timber
Suitable for light greenhouses of small size. A big minus of such a foundation is a short service life, about 5-7 years. However, if you have access to a tree or the opportunity to purchase material inexpensively, then this problem is not so terrible.
brick foundation
The brick foundation is much more reliable and durable wood. The service life of such a foundation is limited only by the location of the structure, the quality of the brick and the work performed on the laying. The brick is laid on a small concrete pillow. At the same time, it is necessary to use a waterproofing, since the moisture spoils the material quite quickly. The masonry can also be shed on both sides with cement mortar to a depth of about 30 cm. This will give the foundation strength and extend its service life.
foundation stone
This type of foundation is worth using for heavy structures with a polycarbonate or glass coating, and if the greenhouse is not planned to be moved the next 10-15 years. The stone foundation is expensive, laborious, but, at the same time, the most reliable option. The foundation of the stone not only gives the base of the greenhouse maximum rigidity, but also protects the inner space from the impact of the environment. However, due to the high cost and complexity of work, this type of foundation is used infrequently.
concrete strip foundation
This is the most common construction for most buildings, including residential buildings. Such a foundation is perfect for all types of greenhouses and their construction. Make it fairly simple, even on its own, it will cost a little, and will be guaranteed to last at least 10 years.
Belt foundation width of 30-40 cm is poured to a depth of 50-60 cm. The foundation of such dimensions will be enough not only for a greenhouse made of polycarbonate or glass, but also for a small shed or tent. At the bottom of the trench, pour a pillow of gravel or sand, set the formwork, inside which you can put a reinforcing bar for rigidity, then the formwork is poured with mortar. The foundation must rise above the ground by at least 20-30 cm.
Types of frameworks for greenhouses
Greenhouse frames are made of plastic, steel, wood, aluminum, etc. each material has its pros and cons
plastic frame
Expensive, but very high quality construction. Very low thermal conductivity. Used infrequently in view of the high cost.
wooden frame
Wood is the first material that was used for greenhouse frameworks. In terms of work is very convenient, well-kept heat, but short-lived. Due to the fact that in the greenhouses, mainly grow edible plants, the wooden frame can not be impregnated with protective compounds.
steel frame
Broken and durable. Other advantages include relatively low cost and ease of construction. Among the shortcomings can be noted the inability to create original forms of greenhouses and the need to use only glass and polycarbonate coating.
aluminum frame
Does not rust, durable, lightweight, durable, stable. If necessary, it is always possible to add new elements to the aluminum frame, if necessary.
We hope that the material in this publication will help you choose a good greenhouse that will delight you with fresh vegetables and greens all year round. More information about greenhouses can be found in the video below: