What is not done today from such seemingly banal material as plywood. This and any interior items - furniture, interior partitions, and even bathrooms and sinks. Plywood is environmentally friendly, very durable, practical, convenient to use, has an attractive appearance. In this article we will consider in detail this building material, its types, characteristics, applications, etc. Separate attention should be paid to laminated plywood, which we will also discuss in detail below.
Content
Classification of plywood
Plywood - multi-layer building material, consisting of several layers of veneer glued together. When gluing plywood, an odd number of veneer sheets (from 3 pieces) is used. For additional strength, the veneer layers are perpendicular to each other along the layers of wood.
Plywood is classified according to several parameters:
In the direction of the fibers:
• Longitudinal (fibers on the front side are directed along the sheet).
• Transverse (fibers directed across the sheet).
By function:
• Construction.
• Industrial.
• Packaging.
• Constructional furniture.
By the type of impregnation: FOF, FSF, FC, FB, BS, BV.
• FOF - moisture resistant plywood.
• PSF - plywood with high moisture resistance - it is used for resin phenol-formaldehyde glue. From the plywood PSF mounted laminated formwork for monolithic storey construction.
• FC - plywood, which has an average moisture resistance. In production, carbamide glue is used. It is most often used for interior decoration of rooms and furniture.
• FB - before gluing, the veneer sheets are impregnated with bakelite varnish. This kind of plywood is maximum resistant to environmental influences. Plywood FB can be used in tropical climates, under conditions of high humidity, and even under water.
• BS - the plywood is impregnated with bakelite alcohol-soluble glue. It has unique properties for plywood: great strength, excellent resistance to all kinds of aggressive environments, elasticity, flexibility, waterproof, does not rot, does not exfoliate, does not become deformed. Another name for this plywood is "aviation" because of the specifics of its use - in aircraft and shipbuilding.
• BW. This brand is impregnated with bakelite glue brand B (water-soluble). The properties of this brand are practically the same as in the BS, except for resistance to moisture.
By type of material:
• Birch.
• Coniferous.
By number of layers:
• Three-layer.
• Five-layer.
• Multilayered.
As we already mentioned above, when gluing a sheet of plywood an odd number of layers of veneer is used: due to this they are placed symmetrically to the middle layer. If the plywood is glued from four layers of veneer, the inner layers are laid perpendicular to the outside to increase the strength of the product.
By type of processing:
• Uncoated plywood (NSH).
• Plywood polished on one side (Ш1).
• Plywood sanded on both sides (Ш2).
plywood grades
In accordance with GOSTs today, plywood is divided into five varieties. Each variety is characterized by the presence of defects and their number.
Grade E is an elite grade of plywood. Defects are not allowed. As an exception, small changes can be permissible, which are explained by the peculiarities of the structure of the wood.
Grade I - minor surface and cracks are permissible, the size of which does not exceed 20 mm.
Grade II - cracks up to 20 cm long can occur, small inclusions of wood and fragments of glue that appeared on the surface, but not more than 2% of the total area of the sheet.
Grade III - wormholes are allowed, the diameter of which is not more than 6 mm, the number is up to 10 pieces per m². The total number of such damages should not exceed 9 pieces per one sheet of plywood.
Variety IV - Plywood of the lowest quality. There may be wormholes with a diameter of no more than 6 mm, the number should not exceed 10 pieces per 1 m².
The plywood of this class may also contain the following defects: fused, blackened and dropped knots in unlimited quantities, wormholes with a diameter of up to 40 mm, defects in the edge of the plywood sheet with a depth of up to 5 mm.
plywood production technology
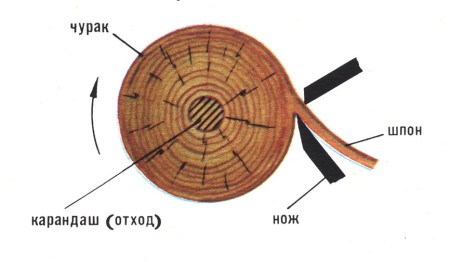
Pre-cleaned from the bark and processed log (churak) is fixed in the machine and rotates around its axis. To the log is brought a special grinding knife, the width of which is equal to the length of the log. With the help of a knife from a log, the "shavings" -spinner is removed. After that, the veneer is cut, dried, sorted and packaged.
The veneer layers are shifted perpendicular to the wood fibers. Each even layer of veneer is covered with adhesive composition on four sides, after which veneer packs are exposed to temperature under high pressure in the press. The finished plywood is adjusted to the required dimensions and packed. As an additional treatment, plywood can be sanded or laminated with a film, which will give the material additional strength and resistance to moisture.
Laminated plywood
Laminated plywood is in great demand in the modern market of building materials. A protective film is applied to the surface of the plywood on one or both sides, a water-repellent acrylic paint is applied to the ends of the sheet. Plywood moisture resistant laminated - a durable and durable material, simple and easy to use.
Technical characteristics of the material:
Among other types of plywood laminated has a number of advantages:
• Increased water resistance, resistance to fungal attack and exposure to aggressive chemical environments.
• Exact dimensions of the sheet.
• Simplicity and ease of handling and installation.
• Wide choice of colors and shades of the sheet surface.
• Different type of sheet surface: smooth (F), mesh (W), paper surface for painting (SP).
• Long service life - laminated plywood moisture resistant for formwork can be used up to 100 times.
The excellent quality of laminated plywood is explained by the fact that only two varieties are allowed for sale: elite grade E - without worm holes, knots, damages and rejects, and 1st grade, allowing only the slightest defects (3 holes with a diameter of not more than 6 mm, up to 5 knots with a diameter of 15 mm per 1 m²).
The material has very high performance characteristics also thanks to the water-repellent glue that connects the layers of veneer in the sheet. Additional strength and protection from premature wear to the material is given by a special film that is glued from one or both sides of the sheet by means of a press and under the influence of high temperature. The denser the film, the more reliable the sheet of plywood is protected.
The composition of the protective film often includes phenol-formaldehyde mixtures or melamine, which increases the wear resistance of the material. Such a cladding is considered toxic and is only used if plywood is used to make formwork in monolithic works.
Plywood laminated for formwork: dimensions, sheet thickness
The thickness of the plywood sheet depends on the number of layers of pressed veneer. For example, in a sheet of laminated plywood 6.5 mm thick. contains 5 layers of veneer:
• 12 mm - 9 layers.
• 15 mm - 11 layers.
• 18 mm-13 layers.
• 21 mm - 15 layers.
• 24 mm - 17 layers, etc.
Laminated plywood sheets, according to the requirements of GOST, are produced in such sizes:
• 1525x3050.
• 1500х3000.
• 1250x2500.
• 1220x2440.
The thickness of the sheets can be different: 6-9-12-15-18-21-24-27-30-35-40 mm.
The deviation in the thickness of the plywood sheet within 1-2 mm is allowed.
Where is laminated plywood used?
The material of domestic production is made, mainly from birch. The quality of birch plywood makes it possible to use it for manufacturing formwork for pouring concrete in monolithic works. The plywood of the domestic manufacturer can easily withstand from 40 to 60 pouring cycles for floor monolithic construction.
The Chinese plywood laminated for formwork is also very popular among consumers, the price is much lower than domestic and European counterparts. However, no other advantages, except for low cost, Chinese plywood does not have and can withstand no more than 5-20 pouring cycles. Chinese material is used most often for pouring foundations.
The most durable and high-quality laminated plywood is produced in Finland. Plywood for the formwork produced in Finland can withstand 100 or more cycles of pouring concrete.
As already mentioned above, laminated plywood is most often used in the construction of reusable formwork in monolithic construction for pouring floors, pylons, columns, capital walls, as well as for the construction of bridges, tunnels, etc. At the same time, high-quality plywood with a thickness of at least 18 mm is used. format 1500x300 and 1220x2440 mm - depending on the thickness of the overlap, and, accordingly, the load on the formwork.
In the construction industry, laminated plywood is also used for:
• Construction scaffolding.
• Fences and all sorts of fences.
• Manufacture of furniture, doors and interior partitions.
• Coatings for the floor.
Plywood foundation formwork
Below, we describe one of the simplest options for constructing plywood formwork for pouring the foundation of a private house.
First trenches dig into the required depth. Under the pile-and-tape foundation, holes are drilled along the bottom of the trenches, after which the bottom of the trenches and boreholes is sprinkled with a layer of sand that is rammed, after which the bottom is checked with a level and, if necessary, leveled.
Then the formwork is mounted. Laminated plywood for formwork is located on both sides of the trench, parallel to each other. Thus, sheets are laid all around the perimeter of the future building, under the capital walls, etc.
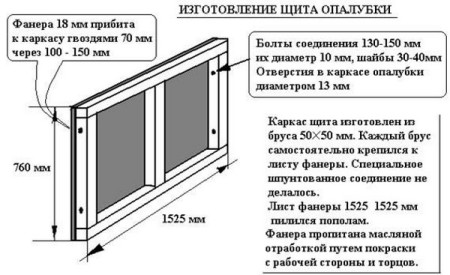
An example of a formwork panel made of plywood in the image:
To plywood does not move under the pressure of concrete, it is fastened with spacers, braces, internal and external jumpers, which are held together by two opposite sheets.
In addition, the sheets are fastened with metal threaded studs, on which wide washers are screwed on both sides.
On the studs, they cut the plastic tube, otherwise the pin can not be removed from the frozen concrete, and the pin is easily removed from the tube. The tube itself remains in the concrete. To ensure that the studs do not tighten the sheets of plywood with each other more than necessary, between the sheets insert wooden bars, the width of which corresponds to the thickness of the foundation.
The side walls of the plywood sheets are additionally reinforced with wooden strips in several rows. In the slats and veneer holes are drilled a bit more than 10 mm, into which metal studs are subsequently inserted and fastened together with the slats.
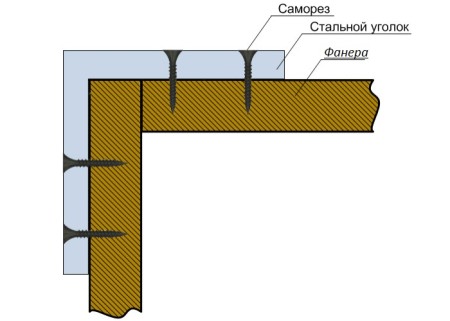
If the foundation is low, the slats are installed only at the top and bottom of the sheets. For high foundations, another one is opened, in the middle. Places of angular joints of plywood are connected by angular brackets which are fastened by screws.
All forms of formwork must be done only from the outside. Nails are clogged from the inside, the ends are bent from the outside - the inner part of the formwork should be smooth.
Important point: if the plywood has been repeatedly used for pouring, the inner part of the formwork must necessarily be treated with linseed oil or at least used engine oil - otherwise a sheet with an insufficiently smooth surface will be very problematic to tear off the frozen concrete.
Before pouring, all the cracks between the plywood sheets are carefully sealed to prevent liquid concrete from flowing out. For additional protection of the formwork, metal clamps can be worn on top of it, and wooden or metal stakes are clogged from the outside to the plywood, the upper parts of which are pulled together by wire. After the concrete has solidified, the formwork is carefully disassembled, after which the plywood sheets can be reused.