Many gardeners are faced with the problem of close groundwater in their dacha section. And this is really a big difficulty for the summer resident, because this misfortune can undo all efforts to grow a good harvest. But let's stop now and say that we can and must fight with groundwater. And here's how - we'll talk about this later in our article. But do not forget that this work is dirty, laborious. Therefore, take care of the overalls in advance, help to solve this issue http://specteks-plus.ru/.
Content
Groundwater is good or bad?
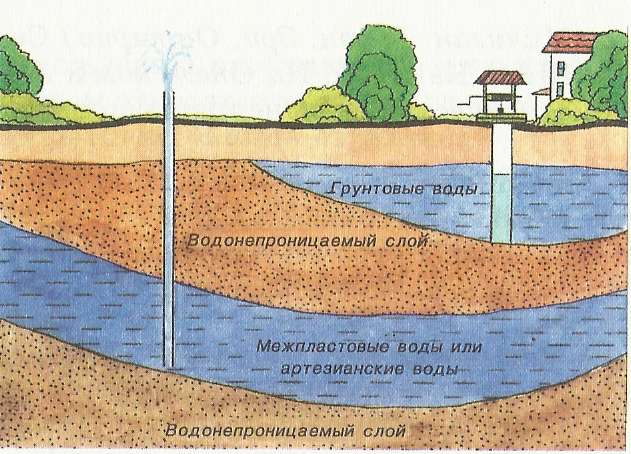
Someone might ask: "Well, why is this article wearing such a strange name? Is the groundwater - is it bad? After all, water for plants in the suburban area (as for all living things) is life! "Yes, we do not argue - water brings life to all life on our Planet. But this is only in general. And in particular, in conditions of close lying to the surface of groundwater on the site - this is disastrous for the garden. Why? Yes, because according to statistics, your health-blossoming cherry will turn into a dead shrub in a month, and the apple tree - in forty-five days, where there will be a spring rise in the level of groundwater near the surface of the soil. Earnestly? Then let's fight them!

How to determine the level of groundwater in the area
The enemy must be known in person. So let's define it! If there is any structure in the summer residence, especially with a cellar (garden house), the groundwater will manifest itself in the first spring. As soon as the movement of water in nature begins - here they are, here, here as here! But what to do when there is no building? When the first building, which is planned to be built here, is our country house? Then we will not take risks, but we will find out everything and the rhinestone.

To begin with, watch the trees. The higher the trees, the lower the groundwater in this particular area. It is very good for building a house, laying a garden and for making a deep dry cellar.

In those places where the groundwater is very close to the surface, the branches are underdeveloped, and the tips have withered tips. You can also observe completely dead knots, as well as dead tops of fruit trees. This is very bad. If possible, you do not need to break a garden on this site. And you have to do without a cellar!
Pay attention also to the grass. In the area where the shallow groundwater table, the grass is very bright and juicy (compared to neighboring areas). In the water-rich soil, plants such as willow, alder, tavolga, willow, sedge, cattail, not to mention cane and horsetail, as well as forget-me-nots, sorrel, nettles and wild currants can be observed.

For plants, you can even find out the approximate depth of the location of groundwater from the soil surface. Where reeds grow, groundwater lies at a depth of one to three meters, a cattail to one meter, poplar black from half a meter to three, reeds from zero to one and a half meters (sometimes up to three to five), wormwood from three up to five (sometimes up to seven meters), licorice - from one and a half to five (or up to ten) meters, and alfalfa is yellow from one and a half to two (or ten to fifteen) meters. Cranberry also grows well on marshy soil.

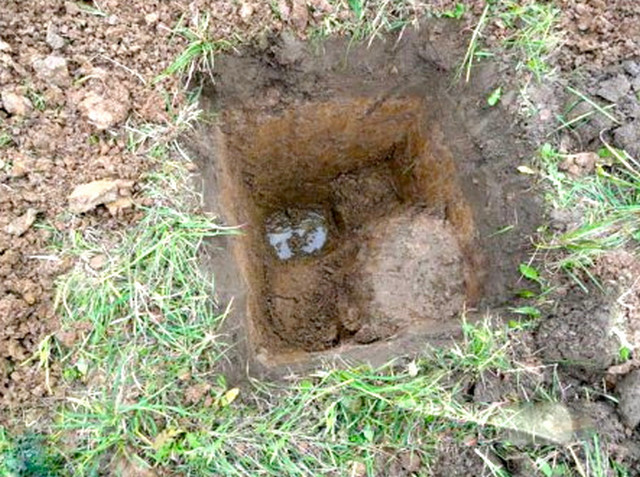
You can use a more accurate, measuring method. In the spring, when the water table is the highest, drill a hole in the soil. For this purpose, it is best to use a drill not less than two meters long, with the marks marked on it (see). Thus, you will learn how close to the surface of the soil are the groundwaters.

So, the main thing to find out in advance is what is on the surface - sand or clay? What is the depth at which the layers change and what is their thickness? The level of location of groundwater (season and weather during this measurement) and the water saturation of the layers of land of the site of interest to us?

But where can we find answers to such difficult questions for the common man in the street? How to determine how dangerous groundwater is to our garden? In fact, everything is very simple. You can try to find out everything yourself, by the method of experiments and calculations. About how to do this, we wrote a little earlier - you can drill a well and dig a hole in the garden area. You can also try to ask about this nearby neighbors. Perhaps they can tell us a lot of useful things from their practice.

In any case, be careful, and do not do what you will later regret - if possible, do not break the garden in a land where the groundwater is very high, do not build a house on such a land and dig out the cellar.
How to deal with groundwater at the site
But what to do for those who do not have any choice - the groundwaters are in close proximity to the soil surface, and from two variants of their occurrence - low and high, did you drop the first option? There's nothing to be done - we'll have to fight them! But how? Let's find out.
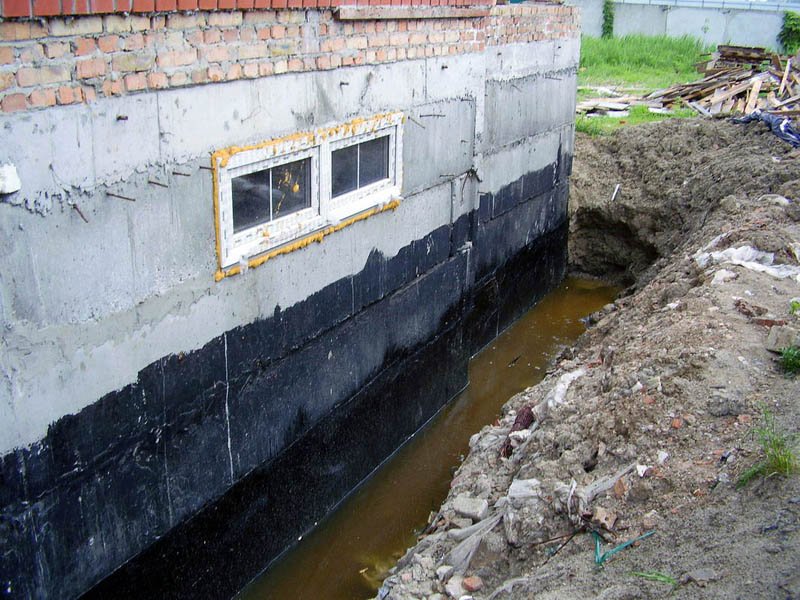
With the groundwater in the country, you can fight by dewatering. If the groundwater table is high, then special ditches around the land area can help. And not just ditches, but a whole network of reclamation ditches will help us reduce the level of groundwater and avoid waterlogging of buildings and death of plants. But how can this help, and is it really effective? Well, of course! Think for yourself - the ground water from all ends of the garden area starts to flow into the ditches because now they are those only places in the suburban area where there is no soil resistance and the capillary rise of the liquid is upwards missing (this is physics). To better understand this unique and very useful process for us, take a look at the picture below.
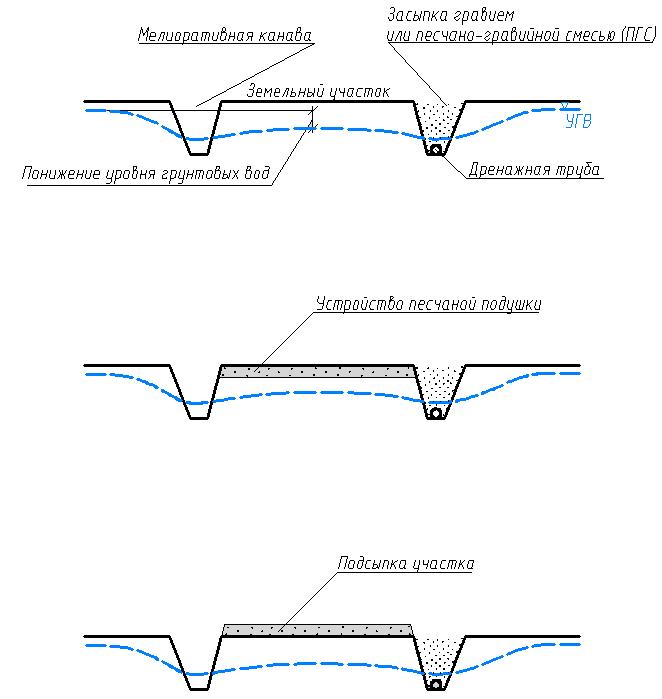
Also note that it is not enough to dig such meliorative canals around the garden plot, it is still necessary to ensure a complete drainage of water from them (otherwise there will be no sense).
To the walls of our drainage ditches do not creep, you can pour rubble or gravel into the ditches, or fill them with a mixture of sand and gravel, first putting drainage pipes on the bottom of the ditches.
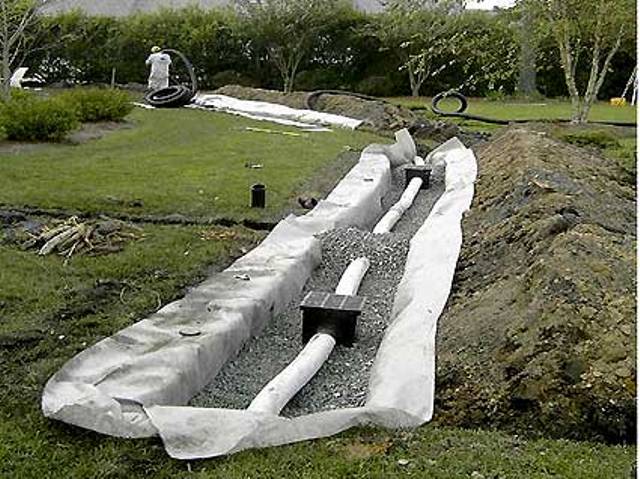

In addition to everything else, it would be nice to deploy our struggle with groundwater in the garden area, and to carry out a set of special measures to increase the level of the foundation of the buildings and, in parallel, lower the level of groundwater.
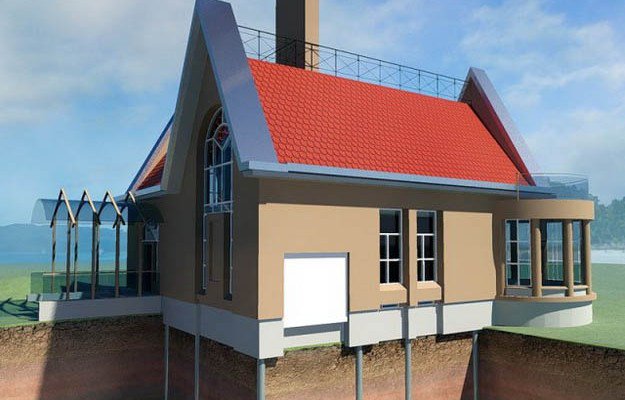

For example, after making meliorative canals, do not stop there, and also completely raise (by padding) the level of the entire garden area and the foundation of the country house.

In any case, especially when complex situations arise, the consultation of a qualified specialist will never be a hindrance.
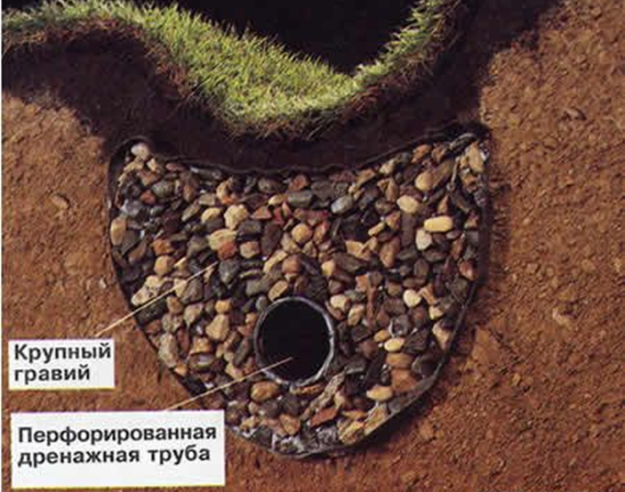

So, is close or, on the contrary, low ground water in the suburban area - the problem is solvable, there would be only a desire! About this in conclusion, we bring to your attention a small video.